elisa test and types|types of elisa methods : specialty store Types of ELISA and ELISA test diagram. The ELISA was originally conceptualized, independently, in 1971 by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlman 3 at Stockholm University in Sweden, and Anton Schuurs and Bauke van Weemen 4 in the Netherlands. They sought an immunoassay method able to detect the presence of antigens or antibodies to . Most structural heart conditions have been traditionally treated with open heart operations, but advances in structural heart disease make it possible now to treat many of these problems with minimally invasive approaches.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sterilizers/Autoclaves; Midmark - Ritter M7; Documents; User's Guide; Midmark Ritter M7 User's Guide
types of elisa methods
ELISA. The enzyme system of ELISA consists enzyme which is labeled to a specific antibody or antigen and a chromogenic substrate that is added after the antigen-antibody reaction. The substrate is hydrolyzed by the enzyme attached to antigen-antibody complexes. An ELISA test uses components of the immune system (such as IgG or IgM antibodies) and . ELISA, short for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a widely used laboratory technique that detects and measures the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample. It involves the binding of target molecules (antibodies or antigens) to a solid surface, followed by the addition of enzymes or fluorescent markers to generate a detectable signal. ELISA is . Types of ELISA Test. There are four basic ELISA formats, allowing for a certain amount of flexibility which can be adjusted based on the antibodies available, the results required, or the complexity of the samples: 1.Direct ELISA 2.Indirect ELISA. 3.Sandwich ELISA Types of ELISA and ELISA test diagram. The ELISA was originally conceptualized, independently, in 1971 by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlman 3 at Stockholm University in Sweden, and Anton Schuurs and Bauke van Weemen 4 in the Netherlands. They sought an immunoassay method able to detect the presence of antigens or antibodies to .
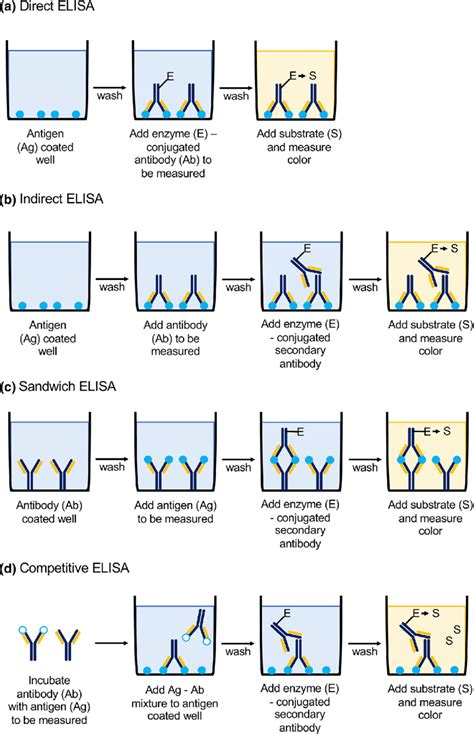
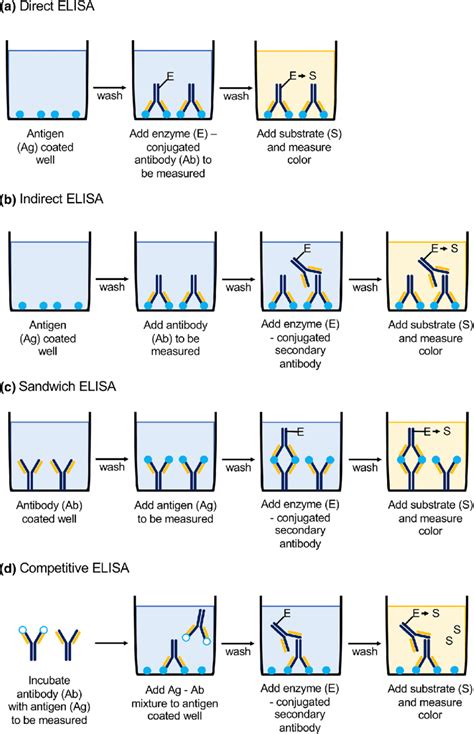
The diagram below illustrates the four main different types of ELISA. Figure 2. The different types of ELISA (direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive). Direct ELISA. The antigen is immobilized on the surface of the multi-well plate and detected with an antibody specific to the antigen that is directly conjugated to HRP or another detection . This type of ELISA utilizes two specific antibodies, an enzyme-conjugated antibody and another antibody present in the test serum (if the serum is positive). • This type of ELISA depends on the competitive reaction between the sample antigen and antigen bound to the wells of microtiter plate with the primary antibody.
is the sift test hard
This type of ELISA uses two antibodies that sandwich the antigen between them. The first antibody is the capture antibody which is immobilized on the surface of the multiple-wells micro-titer plate. . This method tests for the presence of the specific antigen in the sample of interest. Protocol. Immobilization of the Capture Antibody. The .Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay widely used in basic science research, clinical application studies, and diagnostics. The ELISA technique relies on the interaction between the antigen (i.e., the target protein) versus .The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (/ ɪ ˈ l aɪ z ə /, / ˌ iː ˈ l aɪ z ə /) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. [1] The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the ligand to be .Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a widely established technology to detect the presence of antigens in samples. Whether you are considering setting up your own ELISA or use one of our ELISA kits, you will find all the information you need in here.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological technique extensively used in research and clinical laboratory settings to quantitatively identify a specific protein (i.e., the antigen or biomarker) in a biological matrix while relying on the principle of the specific binding interaction between the antigen and the antibody against the antigen of interest .ELISA is an abbreviation for "enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay." In 1974, P. Perlmann and E. Engvall developed the test as a substitute for certain radioimmunoassay tests, and eventually, it replaced the western blot test for HIV confirmation. The ELISA test is versatile and medical professionals can perform it easily as compared to other more complicated tests; many .
This review describes ELISA methodology, the types of ELISA, their advantages and disadvantages, and a listing of some multifaceted applications both in clinical and research settings, including screening for drug use, pregnancy testing, diagnosing disease, detecting biomarkers, blood typing, and detecting SARS-CoV-2 that causes coronavirus .ELISA Formats The first step in an ELISA experiment is the immobilization of the antigen in a sample to the wall of the wells of a microtiter plate. This can be achieved by direct adsorption to the plate’s surface or by using a “capture antibody”. The capture antibody has to be specific to the target antigen and is mainly used in a specific ELISA type called “sandwich ELISA”.ELISA test stands for Enzyme–Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It is a type of serological test and immunoassay technique. In the ELISA test, an enzyme links to the antibodies particularly to detect the presence of proteins like antigens. The ELISA method was evolved from the RIA technique in .ELISA is now the commonly gold standard for protein detection. Different types of ELISA tests have been developed, respectively direct ELISA, indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA and competitive ELISA .
Direct ELISA was first developed in 1971, it set the base style for other types of ELISA with modifications. In this technique, antibody or antigen was immobilised on a microtiter plate, enzyme-conjugated antibodies were allowed to react followed by colour development with appropriate substrates which was measured.
The purity of the sample may dictate which type of ELISA is suitable. A complex and heterogeneous sample, such as blood, will be best suited to competitive or sandwich ELISA. . signal, compared to the standard control that is only in standard diluent. These issues are known matrix effects. To test if matrix effects are affecting an ELISA, a .
There are different types of ELISA tests you can conduct, and here are some of them: Direct Elisa Test. In this type of test, the tests only use primary antibody-labeled enzymes, meaning there is no need for secondary enzymes and antibodies. The enzyme is subjected to the plate and then reacted with the substrates to produce the desired visible .Possibility to test various sample types: ELISA allows you to run multiple samples at the same time, such as serum, plasma, cellular and tissue extracts, urine, and saliva among others. Quantitative: ELISA is a great tool to determine the concentration of antigens or analytes in a . ELISA- Principle, Types and Applications. ELISA is an antigen antibody reaction. In 1971, ELISA was introduced by Peter Perlmann and Eva Engvall at Stockholm University in Sweden. . Competitive ELISA; This test is used to measure the concentration of an antigen in a sample. In this test, antibody is first incubated in solution with a sample .
types of elisa diagram
May be used to test various sample types: serum, plasma, cellular and tissue extracts, urine, and saliva, among others. These are the general ELISA advantages and disadvantages . There are other advantages and disadvantages depending on the type of ELISA used as explained in the next section. AB0039 202407 B 6 Types of ELISAto the target antigen and is mainly used in a specific ELISA type called “sandwich ELISA” . After immobilization, a detection antibody is added, which binds to the adsorbed antigen . An example of a competition ELISA to test for antigen based on the direct detection method is shown in Figure 5 . Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid .
We describe the different types of ELISAs, the advantages and disadvantages of each and what to consider before choosing an ELISA technique. . An example of a competition ELISA to test for antigen based on the direct detection method is shown in figure 4. In this example, a known antigen is used to coat a multiwell plate. .Types There are many ELISA tests for particular molecules that use the matching antibodies. ELISA tests are broken into several types of tests based on how the analytes and antibodies are bonded and used. The major types are described here. Direct ELISA. The steps of direct ELISA follows the mechanism below:What Does ELISA Do? ELISAs deliver a simple, robust, and cost-effective method to analyze and quantify one or more antigens from a variety of sample types, such as cell lysate, tissue lysate, or serum. ELISA is a popular technique for research and diagnostic samples and can be used as both a single sample test or high throughput method for . Types of ELISA. There are three types of ELISA tests that are distinguished on the basis of methods used for binding between antibodies and antigens- . ELISA is one of the easiest test that can be done quickly and rapidly and it requires any type of sample from the patient. The entire process includes :
elisa principle and types
elisa flow chart
Pilot Rotary Sterilizers (including Steritort) by JBT enable processors to accurately design thermal processes and conduct trials in a pilot plant environment.
elisa test and types|types of elisa methods